RocketMQ消息投递策略
前言 RocketMQ的消息投递分分为两种:一种是生产者往MQ Broker中投递;另外一种则是MQ broker 往消费者 投递(这种投递的说法是从消息传递的角度阐述的,实际上底层是消费者从MQ broker 中Pull拉取的)。本文将从模型的角度来阐述这两种机制。
RocketMQ的消息模型
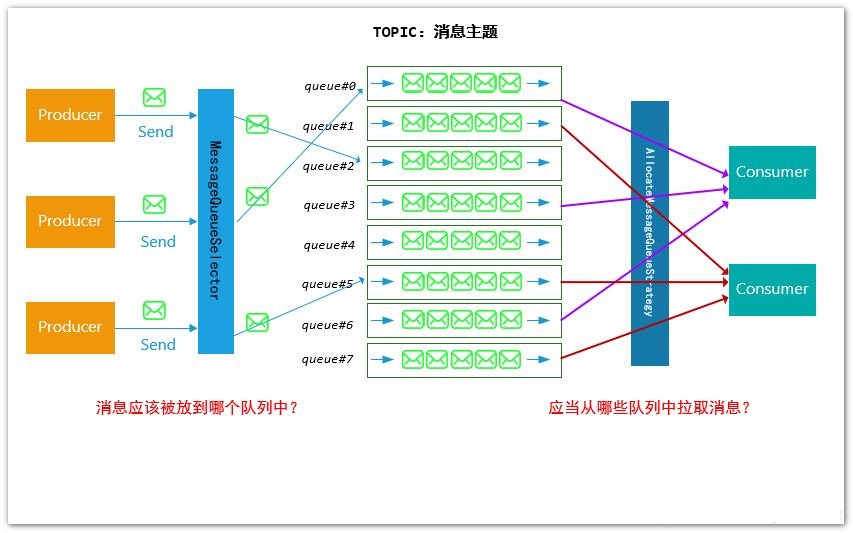
RocketMQ 的消息模型整体并不复杂,如下图所示:
一个Topic(消息主题)可能对应多个实际的消息队列(MessgeQueue)
在底层实现上,为了提高MQ的可用性和灵活性,一个Topic在实际存储的过程中,采用了多队列的方式,具体形式如上图所示。每个消息队列在使用中应当保证先入先出 (FIFO,First In First Out)的方式进行消费。
那么,基于这种模型,就会引申出两个问题:
生产者 在发送相同Topic的消息时,消息体应当被放置到哪一个消息队列(MessageQueue)中?消费者 在消费消息时,应当从哪些消息队列中拉取消息?
消息的系统间传递时,会跨越不同的网络载体,这会导致消息的传播无法保证其有序请
生产者投递策略 轮询算法投递
默认投递方式:基于Queue队列轮询算法投递
默认情况下,采用了最简单的轮询算法,这种算法有个很好的特性就是,保证每一个Queue队列的消息投递数量尽可能均匀,算法如下图所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName); } public class TopicPublishInfo { private volatile ThreadLocalIndex sendWhichQueue = new ThreadLocalIndex (); public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final String lastBrokerName) { if (lastBrokerName == null ) { return selectOneMessageQueue(); } else { int index = this .sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement(); for (int i = 0 ; i < this .messageQueueList.size(); i++) { int pos = Math.abs(index++) % this .messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; MessageQueue mq = this .messageQueueList.get(pos); if (!mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) { return mq; } } return selectOneMessageQueue(); } } public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue () { int index = this .sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this .messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; return this .messageQueueList.get(pos); } }
代码示例
RocketMQ默认采用轮询投递策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class PollingProducer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer ("rocket_test_consumer_group" ); producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876" ); producer.start(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { Message msg = new Message ( "topicTest" , "TagA" , ("Hello Java demo RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET) ); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg); System.out.println("product: 发送状态:" + sendResult.getSendStatus() + ",存储queue:" + sendResult.getMessageQueue().getQueueId() + ",消息索引:" + i); } producer.shutdown(); } }
打印结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:0,消息索引:0 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,消息索引:1 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:2,消息索引:2 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:3,消息索引:3 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:0,消息索引:4 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,消息索引:5 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:2,消息索引:6 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:3,消息索引:7 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:0,消息索引:8 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,消息索引:9
消息投递延迟最小策略
默认投递方式的增强:基于Queue队列轮询算法和消息投递延迟最小的策略投递
默认的投递方式比较简单,但是也暴露了一个问题,就是有些Queue队列可能由于自身数量积压等原因,可能在投递的过程比较长,对于这样的Queue队列会影响后续投递的效果。
基于这种现象,RocketMQ在每发送一个MQ消息后,都会统计一下消息投递的时间延迟,根据这个时间延迟,可以知道往哪些Queue队列投递的速度快。
在这种场景下,会优先使用消息投递延迟最小的策略,如果没有生效,再使用Queue队列轮询的方式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public class MQFaultStrategy { public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { if (this .sendLatencyFaultEnable) { try { int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement(); for (int i = 0 ; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) { int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos); if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) { if (null == lastBrokerName || mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) return mq; } } final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast(); int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker); if (writeQueueNums > 0 ) { final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); if (notBestBroker != null ) { mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker); mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement() % writeQueueNums); } return mq; } else { latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue" , e); } return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); } return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName); } }
顺序投递策略
上述两种投递方式属于对消息投递的时序性没有要求的场景,这种投递的速度和效率比较高。而在有些场景下,需要保证同类型消息投递和消费的顺序性。
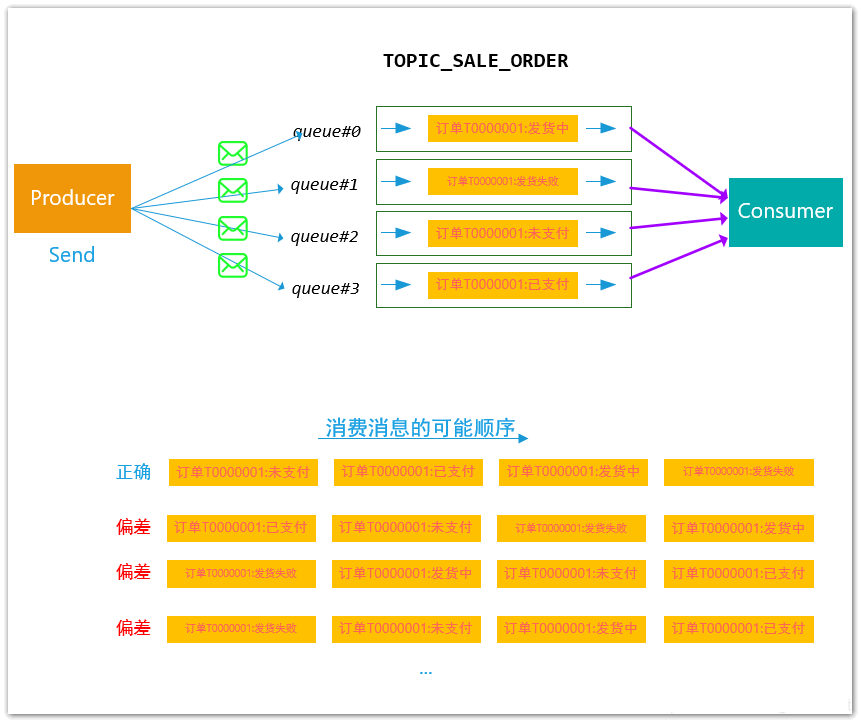
例如,假设现在有TOPIC topicTest,该 Topic下有4个Queue队列,该Topic用于传递订单的状态变迁,假设订单有状态:未支付、已支付、发货中(处理中)、发货成功、发货失败。
在时序上,生产者从时序上可以生成如下几个消息:
1 订单T0000001:未支付 --> 订单T0000001:已支付 --> 订单T0000001:发货中(处理中) --> 订单T0000001:发货失败
消息发送到MQ中之后,可能由于轮询投递的原因,消息在MQ的存储可能如下:
这种情况下,我们希望消费者消费消息的顺序和我们发送是一致的,然而,有上述MQ的投递和消费机制,我们无法保证顺序是正确的,对于顺序异常的消息,消费者 即使有一定的状态容错,也不能完全处理好这么多种随机出现组合情况。
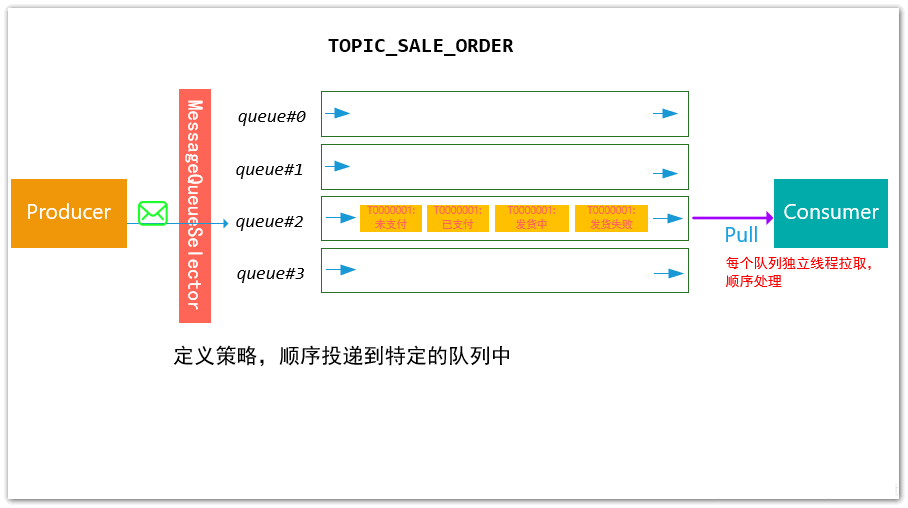
基于上述的情况,RockeMQ采用了这种实现方案:对于相同订单号的消息,通过一定的策略,将其放置在一个 queue队列中,然后消费者再采用一定的策略(一个线程独立处理一个queue,保证处理消息的顺序性),能够保证消费的顺序性
至于消费者是如何保证消费的顺序行的,后续再详细展开,我们先看生产者是如何能将相同订单号的消息发送到同一个queue队列的:
生产者在消息投递的过程中,使用了 MessageQueueSelector 作为队列选择的策略接口,其定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public interface MessageQueueSelector { MessageQueue select (final List<MessageQueue> mqs, final Message msg, final Object arg) ; }
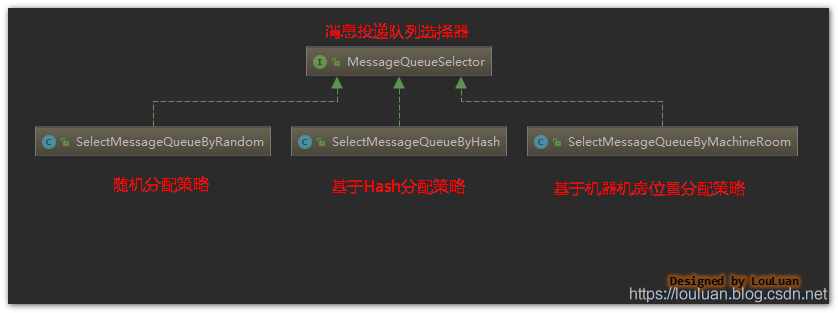
相应地,目前RocketMQ提供了如下几种实现:
默认实现
投递策略
策略实现类
说明
随机分配策略
SelectMessageQueueByRandom
使用了简单的随机数选择算法
基于Hash分配策略
SelectMessageQueueByHash
根据附加参数的Hash值,按照消息队列列表的大小取余数,得到消息队列的index
基于机器机房位置分配策略
SelectMessageQueueByMachineRoom
开源的版本没有具体的实现,基本的目的应该是机器的就近原则分配
现在大概看下策略的代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class SelectMessageQueueByHash implements MessageQueueSelector { @Override public MessageQueue select (List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) { int value = arg.hashCode(); if (value < 0 ) { value = Math.abs(value); } value = value % mqs.size(); return mqs.get(value); } }
代码示例
实际的操作代码样例如下,通过订单号作为hash运算对象,就能保证相同订单号的消息能够落在相同的queue队列上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public class OrderProducer { private static final List<ProductOrder> orderList = new ArrayList <>(); static { orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX001" , "订单创建" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX001" , "订单付款" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX001" , "订单完成" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX002" , "订单创建" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX002" , "订单付款" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX002" , "订单完成" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX003" , "订单创建" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX003" , "订单付款" )); orderList.add(new ProductOrder ("XXX003" , "订单完成" )); } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer ("rocket_test_consumer_group" ); producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876" ); producer.start(); for (int i = 0 ; i < orderList.size(); i++) { ProductOrder order = orderList.get(i); Message message = new Message ( "topicTest" , order.getOrderId(), (order.toString()).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET) ); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(message, new SelectMessageQueueByHash (), order.getOrderId()); System.out.println("product: 发送状态:" + sendResult.getSendStatus() + ",存储queue:" + sendResult.getMessageQueue().getQueueId() + ",orderID:" + order.getOrderId() + ",type:" + order.getType()); } producer.shutdown(); } }
打印结果如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:3,orderID:XXX001,type:订单创建 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:3,orderID:XXX001,type:订单付款 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:3,orderID:XXX001,type:订单完成 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:2,orderID:XXX002,type:订单创建 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:2,orderID:XXX002,type:订单付款 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:2,orderID:XXX002,type:订单完成 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,orderID:XXX003,type:订单创建 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,orderID:XXX003,type:订单付款 product: 发送状态:SEND_OK,存储queue:1,orderID:XXX003,type:订单完成
消费者分配队列
如何为消费者分配queue队列?
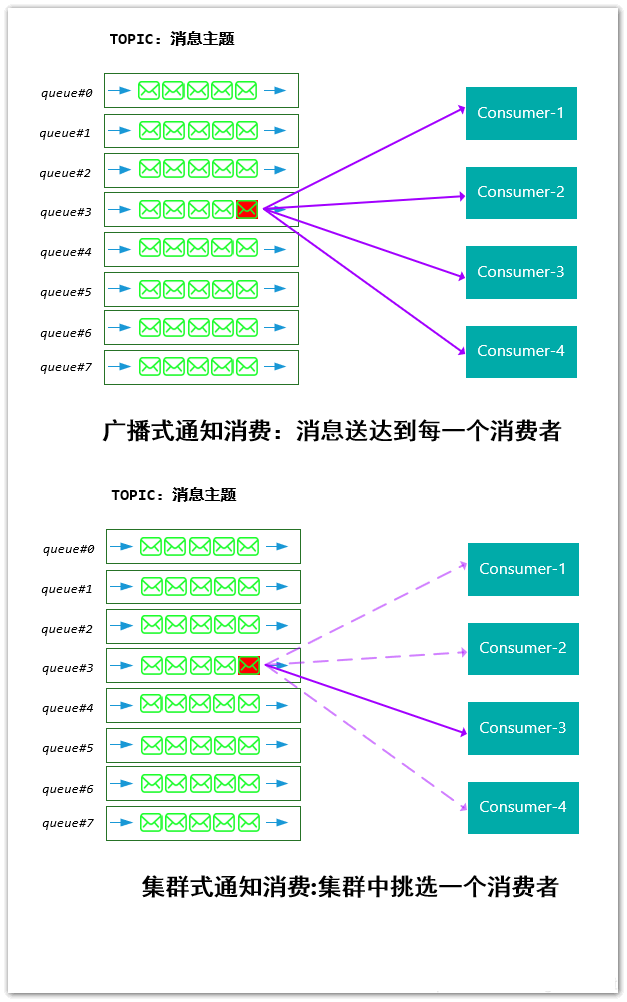
RocketMQ对于消费者消费消息有两种形式:
BROADCASTING:广播式消费,这种模式下,一个消息会被通知到每一个消费者CLUSTERING: 集群式消费,这种模式下,一个消息最多只会被投递到一个消费者上进行消费
广播式的消息模式比较简单,下面我们介绍下集群式。对于使用了消费模式为MessageModel.CLUSTERING进行消费时,需要保证一个消息在整个集群中只需要被消费一次 。实际上,在RoketMQ底层,消息指定分配给消费者的实现,是通过queue队列分配给消费者的方式完成的:也就是说,消息分配的单位是消息所在的queue队列。即:
将queue队列指定给特定的消费者后,queue队列内的所有消息将会被指定到消费者进行消费。
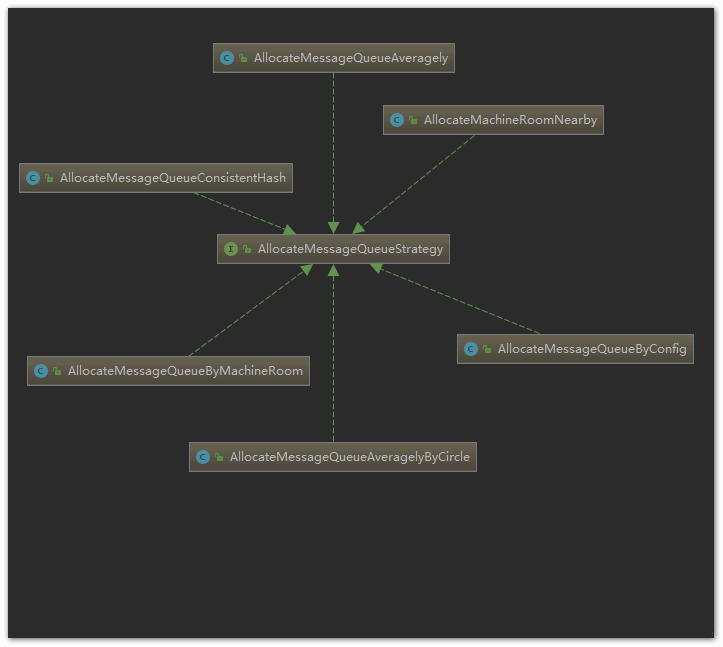
RocketMQ定义了策略接口AllocateMessageQueueStrategy,对于给定的消费者分组,和消息队列列表、消费者列表,当前消费者应当被分配到哪些queue队列,定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public interface AllocateMessageQueueStrategy { List<MessageQueue> allocate ( final String consumerGroup, final String currentCID, final List<MessageQueue> mqAll, final List<String> cidAll ) ; String getName () ; }
相应地,RocketMQ提供了如下几种实现:
算法名称
含义
AllocateMessageQueueAveragely
平均分配算法
AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle
基于环形平均分配算法
AllocateMachineRoomNearby
基于机房临近原则算法
AllocateMessageQueueByMachineRoom
基于机房分配算法
AllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash
基于一致性hash算法
AllocateMessageQueueByConfig
基于配置分配算法
为了讲述清楚上述算法的基本原理,我们先假设一个例子,下面所有的算法将基于这个例子讲解。
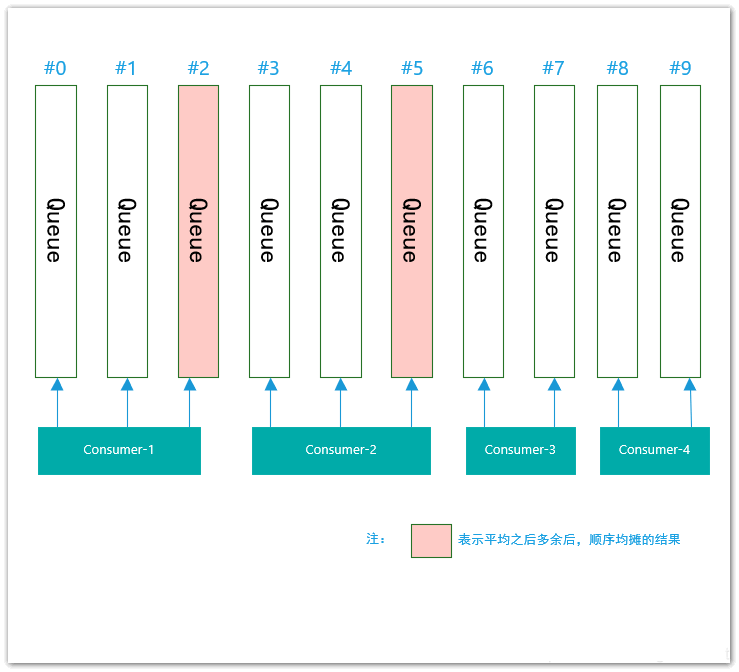
假设当前同一个topic下有queue队列 10个,消费者共有4个,如下图所示:
下面依次介绍其原理:
平均分配算法 这里所谓的平均分配算法,并不是指的严格意义上的完全平均,如上面的例子中,10个queue,而消费者只有4个,无法是整除关系,除了整除之外的多出来的queue,将依次根据消费者的顺序均摊。
按照上述例子来看,10/4=2,即表示每个消费者平均均摊2个queue;而10%4=2,即除了均摊之外,多出来2个queue还没有分配,那么,根据消费者的顺序consumer-1、consumer-2、consumer-3、consumer-4,则多出来的2个queue将分别给consumer-1和consumer-2。
最终,分摊关系如下:
consumer-1:3个
consumer-2:3个
consumer-3:2个
consumer-4:2个
其代码实现非常简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class AllocateMessageQueueAveragely implements AllocateMessageQueueStrategy { private final InternalLogger log = ClientLogger.getLog(); @Override public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { if (currentCID == null || currentCID.length() < 1 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("currentCID is empty" ); } if (mqAll == null || mqAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("mqAll is null or mqAll empty" ); } if (cidAll == null || cidAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("cidAll is null or cidAll empty" ); } List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) { log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}" , consumerGroup, currentCID, cidAll); return result; } int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID); int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size(); int averageSize = mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size() + 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size()); int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod; int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex); for (int i = 0 ; i < range; i++) { result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size())); } return result; } @Override public String getName () { return "AVG" ; } }
演示效果 消费者A 1 2 3 4 Consumer-线程名称=[32],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608171677558],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 2] Consumer-线程名称=[34],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608171677580],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 3] Consumer-线程名称=[36],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608171677655],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 6] Consumer-线程名称=[38],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608171677679],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 7]
消费者B 1 2 3 4 5 6 Consumer-线程名称=[35],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608171677508],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 0] Consumer-线程名称=[36],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171677535],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 1] Consumer-线程名称=[37],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608171677609],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 4] Consumer-线程名称=[38],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171677635],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 5] Consumer-线程名称=[39],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608171677709],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 8] Consumer-线程名称=[40],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171677734],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 9]
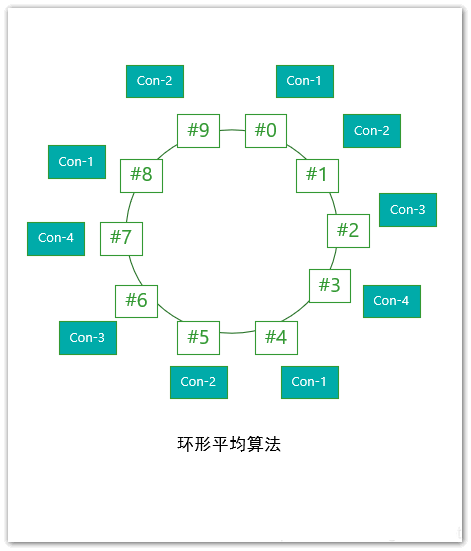
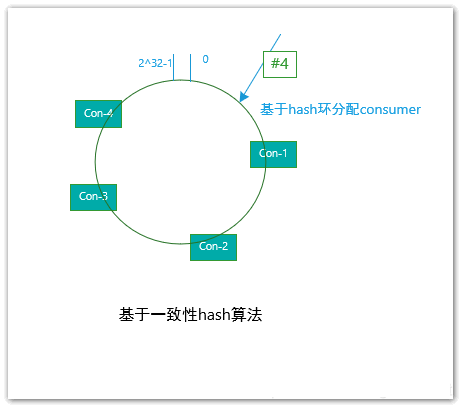
基于环形平均算法
环形平均算法,是指根据消费者的顺序,依次在由queue队列组成的环形图中逐个分配。具体流程如下所示:
这种算法最终分配的结果是:
consumer-1: #0,#4,#8consumer-2: #1, #5, # 9consumer-3: #2,#6consumer-4: #3,#7
其代码实现如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle implements AllocateMessageQueueStrategy { private final InternalLogger log = ClientLogger.getLog(); @Override public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { if (currentCID == null || currentCID.length() < 1 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("currentCID is empty" ); } if (mqAll == null || mqAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("mqAll is null or mqAll empty" ); } if (cidAll == null || cidAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("cidAll is null or cidAll empty" ); } List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) { log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}" , consumerGroup, currentCID, cidAll); return result; } int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID); for (int i = index; i < mqAll.size(); i++) { if (i % cidAll.size() == index) { result.add(mqAll.get(i)); } } return result; } @Override public String getName () { return "AVG_BY_CIRCLE" ; } }
演示效果 设置算法 1 2 DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer (null , "rocket_test_consumer_group" , null , new AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle ());
消费者A 1 2 3 4 5 Consumer-线程名称=[35],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608171903364],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 1] Consumer-线程名称=[38],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608171903411],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 3] Consumer-线程名称=[39],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608171903459],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 5] Consumer-线程名称=[40],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608171903508],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 7] Consumer-线程名称=[41],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608171903562],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 9]
消费者B 1 2 3 4 5 Consumer-线程名称=[28],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171903346],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 0] Consumer-线程名称=[30],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608171903393],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 2] Consumer-线程名称=[32],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171903443],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 4] Consumer-线程名称=[34],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608171903490],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 6] Consumer-线程名称=[36],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608171903540],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 8]
一致性hash分配算法 使用这种算法,会将consumer消费者作为Node节点构造成一个hash环,然后queue队列通过这个hash环来决定被分配给哪个consumer消费者。
其基本模式如下:
一致性hash算法用于在分布式系统中,保证数据的一致性而提出的一种基于hash环实现的算法
算法实现上也不复杂,如下图所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) { log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}" , consumerGroup, currentCID, cidAll); return result; } Collection<ClientNode> cidNodes = new ArrayList <ClientNode>(); for (String cid : cidAll) { cidNodes.add(new ClientNode (cid)); } final ConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode> router; if (customHashFunction != null ) { router = new ConsistentHashRouter <ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt, customHashFunction); } else { router = new ConsistentHashRouter <ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt); } List<MessageQueue> results = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) { ClientNode clientNode = router.routeNode(mq.toString()); if (clientNode != null && currentCID.equals(clientNode.getKey())) { results.add(mq); } } return results; }
演示效果 设置算法 1 2 DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer (null , "rocket_test_consumer_group" , null , new AllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash ());
消费者A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Consumer-线程名称=[29],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608172067310],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 0] Consumer-线程名称=[31],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608172067323],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 1] Consumer-线程名称=[33],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608172067345],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 2] Consumer-线程名称=[37],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608172067395],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 4] Consumer-线程名称=[39],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608172067418],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 5] Consumer-线程名称=[40],接收queueId:[2],接收时间:[1608172067443],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 6] Consumer-线程名称=[41],接收queueId:[0],接收时间:[1608172067494],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 8] Consumer-线程名称=[42],接收queueId:[1],接收时间:[1608172067518],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 9]
消费者B 1 2 Consumer-线程名称=[28],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608172067383],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 3] Consumer-线程名称=[30],接收queueId:[3],接收时间:[1608172067475],消息=[Hello Java demo RocketMQ 7]
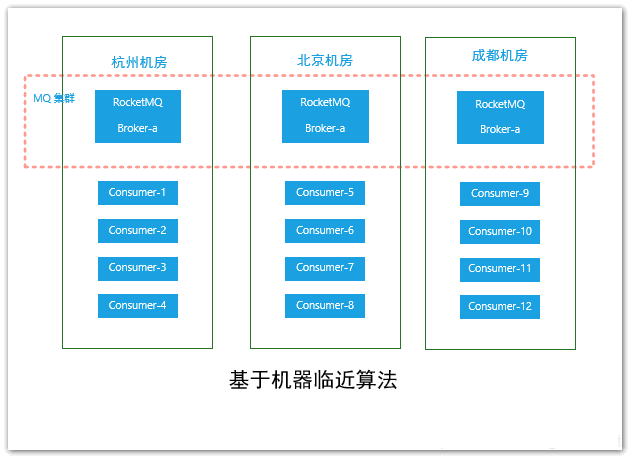
机房临近分配算法 该算法使用了装饰者设计模式,对分配策略进行了增强。一般在生产环境,如果是微服务架构下,RocketMQ集群的部署可能是在不同的机房中部署,其基本结构可能如下图所示:
对于跨机房的场景,会存在网络、稳定性和隔离心的原因,该算法会根据queue的部署机房位置和消费者consumer的位置,过滤出当前消费者consumer相同机房的queue队列,然后再结合上述的算法,如基于平均分配算法在queue队列子集的基础上再挑选。相关代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 @Override public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); Map<String, List<MessageQueue>> mr2Mq = new TreeMap <String, List<MessageQueue>>(); for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) { String brokerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.brokerDeployIn(mq); if (StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(brokerMachineRoom)) { if (mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom) == null ) { mr2Mq.put(brokerMachineRoom, new ArrayList <MessageQueue>()); } mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom).add(mq); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Machine room is null for mq " + mq); } } Map<String, List<String>> mr2c = new TreeMap <String, List<String>>(); for (String cid : cidAll) { String consumerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(cid); if (StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(consumerMachineRoom)) { if (mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom) == null ) { mr2c.put(consumerMachineRoom, new ArrayList <String>()); } mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom).add(cid); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Machine room is null for consumer id " + cid); } } List<MessageQueue> allocateResults = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); String currentMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(currentCID); List<MessageQueue> mqInThisMachineRoom = mr2Mq.remove(currentMachineRoom); List<String> consumerInThisMachineRoom = mr2c.get(currentMachineRoom); if (mqInThisMachineRoom != null && !mqInThisMachineRoom.isEmpty()) { allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqInThisMachineRoom, consumerInThisMachineRoom)); } for (String machineRoom : mr2Mq.keySet()) { if (!mr2c.containsKey(machineRoom)) { allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, mr2Mq.get(machineRoom), cidAll)); } } return allocateResults; }
基于机房分配算法 该算法适用于属于同一个机房内部的消息,去分配queue。这种方式非常明确,基于上面的机房临近分配算法的场景,这种更彻底,直接指定基于机房消费的策略。这种方式具有强约定性,比如broker名称按照机房的名称进行拼接,在算法中通过约定解析进行分配。
其代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public class AllocateMessageQueueByMachineRoom implements AllocateMessageQueueStrategy { private Set<String> consumeridcs; @Override public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); int currentIndex = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID); if (currentIndex < 0 ) { return result; } List<MessageQueue> premqAll = new ArrayList <MessageQueue>(); for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) { String[] temp = mq.getBrokerName().split("@" ); if (temp.length == 2 && consumeridcs.contains(temp[0 ])) { premqAll.add(mq); } } int mod = premqAll.size() / cidAll.size(); int rem = premqAll.size() % cidAll.size(); int startIndex = mod * currentIndex; int endIndex = startIndex + mod; for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) { result.add(mqAll.get(i)); } if (rem > currentIndex) { result.add(premqAll.get(currentIndex + mod * cidAll.size())); } return result; } @Override public String getName () { return "MACHINE_ROOM" ; } public Set<String> getConsumeridcs () { return consumeridcs; } public void setConsumeridcs (Set<String> consumeridcs) { this .consumeridcs = consumeridcs; } }
基于配置分配算法
这种算法单纯基于配置的,非常简单,实际使用中可能用途不大。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class AllocateMessageQueueByConfig implements AllocateMessageQueueStrategy { private List<MessageQueue> messageQueueList; @Override public List<MessageQueue> allocate (String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll, List<String> cidAll) { return this .messageQueueList; } @Override public String getName () { return "CONFIG" ; } public List<MessageQueue> getMessageQueueList () { return messageQueueList; } public void setMessageQueueList (List<MessageQueue> messageQueueList) { this .messageQueueList = messageQueueList; } }
消费者如何指定分配算法 消费者构造方法
在DefaultMQPushConsumer构造方法中可以传入分配策略
默认情况下,消费者使用的是AllocateMessageQueueAveragely算法,也可以自己指定:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class DefaultMQPushConsumer { public DefaultMQPushConsumer () { this (MixAll.DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP, null , new AllocateMessageQueueAveragely ()); } public DefaultMQPushConsumer (final String consumerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook, AllocateMessageQueueStrategy allocateMessageQueueStrategy) { this .consumerGroup = consumerGroup; this .allocateMessageQueueStrategy = allocateMessageQueueStrategy; defaultMQPushConsumerImpl = new DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl (this , rpcHook); } }
我们看到默认使用了AllocateMessageQueueAveragely平均分配策略
使用其他分配策略
如果需要使用其他分配策略,使用方式如下
1 2 3 DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer (null ,"rocket_test_consumer_group" ,null ,new AllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash ());.....