RabbitMQ-SpringBoot整合

简单整合
添加RabbitMQ依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
配置application.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
username: test
password: 123456
|
新建RabbitConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
|
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
public static final String FANOUT_TYPE = "FANOUT";
public static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME = "test_fanout_queue";
public static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME1 = "test_fanout_queue1";
public static final String TEST_FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "testFanoutExchange";
public static final String DIRECT_TYPE = "DIRECT";
public static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_NAME = "test_direct_queue";
public static final String TEST_DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "testDirectExchange";
public static final String DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY = "test";
public static final String TOPIC_TYPE = "TOPIC";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME = "test_topic_queue";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME1 = "test_topic_queue1";
public static final String TEST_TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "testTopicExchange";
public static final String TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY = "test.#";
@Bean
public Queue createFanoutQueue() {
return new Queue(FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME);
}
@Bean
public Queue createFanoutQueue1() {
return new Queue(FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME1);
}
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue() {
return new Queue(DIRECT_QUEUE_NAME);
}
@Bean
public Queue createTopicQueue() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME);
}
@Bean
public Queue createTopicQueue1() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME1);
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange defFanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(TEST_FANOUT_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingFanout() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createFanoutQueue()).
to(defFanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingFanout1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createFanoutQueue1()).
to(defFanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(TEST_DIRECT_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirect() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue()).
to(directExchange()).
with(DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY);
}
@Bean
TopicExchange defTopicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(TEST_TOPIC_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingTopic() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createTopicQueue()).
to(defTopicExchange()).
with(TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingTopic1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createTopicQueue1()).
to(defTopicExchange()).
with(TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY);
}
}
|
新建生产者(producer)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| import com.heima.rabbitmq.config.RabbitConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MsgProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send2FanoutTestQueue(String routingKey, String massage) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.TEST_FANOUT_EXCHANGE,
routingKey, massage);
}
public void send2DirectTestQueue(String routingKey, String massage) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.TEST_DIRECT_EXCHANGE,
routingKey, massage);
}
public void send2TopicTestAQueue(String routingKey, String massage) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.TEST_TOPIC_EXCHANGE,
routingKey, massage);
}
}
|
新建消费者(consumer)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
| import com.heima.rabbitmq.config.RabbitConfig;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
@Component
public class MsgConsumer {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MsgConsumer.class);
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitConfig.FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitConfig.TEST_FANOUT_EXCHANGE, type = "fanout"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processFanoutMsg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到FANOUT消息 : " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitConfig.FANOUT_QUEUE_NAME1, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitConfig.TEST_FANOUT_EXCHANGE, type = "fanout"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processFanout1Msg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到FANOUT1消息 : " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitConfig.DIRECT_QUEUE_NAME, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitConfig.TEST_DIRECT_EXCHANGE),
key = RabbitConfig.DIRECT_ROUTINGKEY)
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到DIRECT消息 : " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitConfig.TEST_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, type = "topic"),
key = RabbitConfig.TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY)
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processTopicMsg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到TOPIC消息 : " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = RabbitConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE_NAME1, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = RabbitConfig.TEST_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, type = "topic"),
key = RabbitConfig.TOPIC_ROUTINGKEY)
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processTopic1Msg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到TOPIC1消息 : " + msg);
}
}
|
编写controller测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitmqController {
@Autowired
private MsgProducer msgProducer;
@RequestMapping("/send")
public String send(String type, String routingKey, String message) {
if (RabbitConfig.DIRECT_TYPE.equals(type)) {
msgProducer.send2DirectTestQueue(routingKey, message);
} else if (RabbitConfig.TOPIC_TYPE.equals(type)) {
msgProducer.send2TopicTestAQueue(routingKey, message);
} else if (RabbitConfig.FANOUT_TYPE.equals(type)) {
msgProducer.send2FanoutTestQueue(routingKey, message);
}
return "OK";
}
}
|
测试
直接交换器测试
单队列绑定
绑定代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue() {
return new Queue("test_direct_queue");
}
@Bean
DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("testDirectExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirect() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue()).
to(directExchange()).
with("test");
}
|
postman测试
postman发送测试请求
1
| http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=DIRECT&routingKey=test&message=测试直接交换器
|
客户端接收到数据
1
| 2020-08-28 10:36:27.014 INFO 16164 --- [ntContainer#0-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到DIRECT消息 : 测试直接交换器
|
如果更换routingKey将收不到数据
多队列绑定不同主题
我们正在用的广播模式的交换器并不够灵活,它只是不加思索地进行广播。因此,需要使用direct exchange来代替。直连交换器的路由算法非常简单:将消息推送到binding key与该消息的routing key相同的队列。
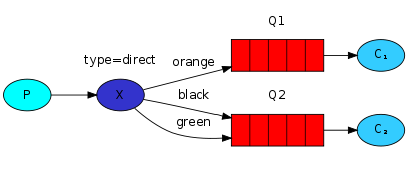
在该图中,直连交换器X上绑定了两个队列。第一个队列绑定了绑定键orange,第二个队列有两个绑定键:black和green。在这种场景下,一个消息在布时指定了路由键为orange将会只被路由到队列Q1,路由键为black和green的消息都将被路由到队列Q2。其他的消息都将被丢失。
绑定代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue() {
return new Queue("test_direct_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue1() {
return new Queue("test_direct_queue1");
}
@Bean
DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("testDirectExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectOrange() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue()).
to(directExchange()).
with("orange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectBlack() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue1()).
to(directExchange()).
with("black");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectGreen() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue1()).
to(directExchange()).
with("green");
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_direct_queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testDirectExchange"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到direct消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_direct_queue1", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testDirectExchange"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg1(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到direct1消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
|
postman测试
1
2
3
| http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=DIRECT&routingKey=orange&message=测试直接交换器orange
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=DIRECT&routingKey=black&message=测试直接交换器black
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=DIRECT&routingKey=green&message=测试直接交换器green
|
日志输出
1
2
3
| 2020-08-28 11:10:28.684 INFO 8284 --- [ntContainer#3-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到direct消息,ROUTINGKEY:orange,message: 测试直接交换器orange
2020-08-28 11:10:52.903 INFO 8284 --- [ntContainer#5-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到direct1消息,ROUTINGKEY:black,message: 测试直接交换器black
2020-08-28 11:11:14.820 INFO 8284 --- [ntContainer#5-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到direct1消息,ROUTINGKEY:green,message: 测试直接交换器green
|
多队列绑定相同主题
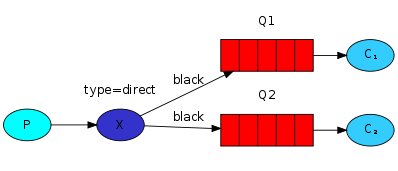
同一个绑定键可以绑定到不同的队列上去,在下图中,我们也可以增加一个交换器X与队列Q2的绑定键,在这种情况下,直连交换器将会和广播交换器有着相同的行为,将消息推送到所有匹配的队列。一个路由键为black的消息将会同时被推送到队列Q1和Q2。
绑定代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue() {
return new Queue("test_direct_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue createDirectQueue1() {
return new Queue("test_direct_queue1");
}
@Bean
DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("testDirectExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectBlack() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue()).
to(directExchange()).
with("black");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectBlack1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createDirectQueue1()).
to(directExchange()).
with("black");
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_direct_queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testDirectExchange"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到direct消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_direct_queue1", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testDirectExchange"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg1(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到direct1消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
|
postman测试
1
| http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=DIRECT&routingKey=black&message=测试直接交换器black
|
日志输出
1
2
| 2020-08-28 11:18:00.069 INFO 5904 --- [ntContainer#2-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到direct消息,ROUTINGKEY:black,message: 测试直接交换器black
2020-08-28 11:18:00.069 INFO 5904 --- [ntContainer#1-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到direct1消息,ROUTINGKEY:black,message: 测试直接交换器black
|
扇形交换器测试
扇形交换机是最基本的交换机类型,它所能做的事情非常简单———广播消息。扇形交换机会把能接收到的消息全部发送给绑定在自己身上的队列。因为广播不需要“思考”,所以扇形交换机处理消息的速度也是所有的交换机类型里面最快的。
绑定代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
@Bean
public Queue createFanoutQueue() {
return new Queue("test_fanout_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue createFanoutQueue1() {
return new Queue("test_fanout_queue1");
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange defFanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("testFanoutExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingFanout() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createFanoutQueue()).
to(defFanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingFanout1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createFanoutQueue1()).
to(defFanoutExchange());
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_fanout_queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testFanoutExchange", type = "fanout"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processFanoutMsg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到FANOUT消息 : " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_fanout_queue1", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testFanoutExchange", type = "fanout"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processFanout1Msg(Message massage) {
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到FANOUT1消息 : " + msg);
}
|
postman测试
1
| http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=FANOUT&routingKey=anykey&message=测试扇形交换器
|
日志输出
1
2
| 2020-08-28 13:46:54.391 INFO 17556 --- [ntContainer#1-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到FANOUT1消息 : 测试扇形交换器
2020-08-28 13:46:54.391 INFO 17556 --- [ntContainer#5-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到FANOUT消息 : 测试扇形交换器
|
主题交换器测试
发送到主题交换器的消息不能有任意的routing key,必须是由点号分开的一串单词,这些单词可以是任意的,但通常是与消息相关的一些特征。比如以下是几个有效的routing key: “stock.usd.nyse”, “nyse.vmw”, “quick.orange.rabbit”,routing key的单词可以有很多,最大限制是255 bytes。
binding key必须与routing key模式一样。Topic交换器的逻辑与direct交换器有点相似:使用特定路由键发送的消息将被发送到所有使用匹配绑定键绑定的队列,然而,绑定键有两个特殊的情况,如下:
- * 表示匹配任意一个单词
- # 表示匹配任意一个或多个单词
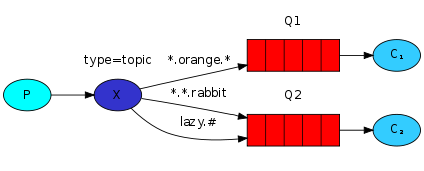
在这个例子中,我们将发送所有跟动物有关的消息,这些消息将会发送到由三个单词,两个点号组成的routing key,第一个单词了表示的是速度,第二个单词表示颜色,第三个单词表示种类:
“<speed>.<colour>.<species>”。
我们创建三个绑定关系:队列Q1绑定到绑定键*.orange.* ,队列Q2绑定到*.*.rabbit和lazy.#。
绑定代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
@Bean
public Queue createTopicQueue() {
return new Queue("test_topic_queue");
}
@Bean
public Queue createTopicQueue1() {
return new Queue("test_topic_queue1");
}
@Bean
TopicExchange defTopicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange("testTopicExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingTopic() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createTopicQueue()).
to(defTopicExchange()).
with("*.orange.*");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingTopic1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createTopicQueue1()).
to(defTopicExchange()).
with("*.*.rabbit");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingTopic2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(createTopicQueue1()).
to(defTopicExchange()).
with("lazy.#");
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_topic_queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testTopicExchange", type = "topic"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processTopicMsg(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到TOPIC消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
@RabbitListener(
bindings =
{
@QueueBinding(value = @Queue(value = "test_topic_queue1", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "testTopicExchange", type = "topic"))
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processTopic1Msg(Message massage) {
String routingkey = massage.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msg = new String(massage.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger.info("接收到TOPIC1消息,ROUTINGKEY:{},message: {}", routingkey, msg);
}
|
postman测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
| http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=quick.orange.rabbit&message=测试主题交换器
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=lazy.orange.elephant&message=测试主题交换器
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=quick.orange.fox&message=测试主题交换器
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=lazy.brown.fox&message=测试主题交换器
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=lazy.pink.rabbit&message=测试主题交换器
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rabbitmq/send?type=TOPIC&routingKey=quick.orangle.male.rabbit&message=测试主题交换器
|
日志输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| 2020-08-28 11:53:31.585 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#3-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC1消息,ROUTINGKEY:quick.orange.rabbit,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 11:53:31.585 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#2-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC消息,ROUTINGKEY:quick.orange.rabbit,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 11:56:07.981 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#3-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC1消息,ROUTINGKEY:lazy.orange.elephant,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 11:56:07.981 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#2-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC消息,ROUTINGKEY:lazy.orange.elephant,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 11:56:34.729 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#2-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC消息,ROUTINGKEY:quick.orange.fox,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 11:57:14.123 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#3-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC1消息,ROUTINGKEY:lazy.brown.fox,message: 测试主题交换器
2020-08-28 12:46:00.455 INFO 5624 --- [ntContainer#3-1] com.heima.rabbitmq.consumer.MsgConsumer : 接收到TOPIC1消息,ROUTINGKEY:lazy.pink.rabbit,message: 测试主题交换器
|
总结
- 队列Q1对橘黄色(orange)颜色的所有动物感兴趣;
- 队列Q2对所有的兔子(rabbit)和所有慢吞吞(lazy)的动物感兴趣。
一个路由为 “quick.orange.rabbit”的消息,将会被转发到这两个队列,路由为”lazy.orange.elephant”的消息也被转发给这两个队列,路由为 “quick.orange.fox”的消息将只被转发到Q1队列,路由为 “lazy.brown.fox”的消息将只被转发到Q2队列。”lazy.pink.rabbit” 只被转发到Q2队列一次(虽然它匹配绑定键*.*.rabbit和lazy.#),路由为 “quick.brown.fox”的消息与任何一个绑定键都不匹配,因此将会被丢弃。
如果我们发送的消息的的路由是由一个单词“orangle”或4个单词”quick.orangle.male.rabbit“将会怎样?会因为与任何一个绑定键不匹配而被丢弃。
另一方面,路由为 “lazy.orange.male.rabbit”的消息,因为匹配”lazy.#”绑定键,因而会被转发到Q2队列。
Topic交换器非常强大,可以像其他类型的交换器一样工作:
当一个队列的绑定键是”#”是,它将会接收所有的消息,而不再考虑所接收消息的路由键,就像是fanout交换器一样;
当一个队列的绑定键没有用到”#“和”*“时,它又像direct交换一样工作。








