JAVA阻塞队列实现
什么是阻塞队列
阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)是一个支持两个附加操作的队列。这两个附加的操作是:在队列为空时,获取元素的线程会等待队列变为非空。当队列满时,存储元素的线程会等待队列可用。阻塞队列常用于生产者和消费者的场景,生产者是往队列里添加元素的线程,消费者是从队列里拿元素的线程。阻塞队列就是生产者存放元素的容器,而消费者也只从容器里拿元素。
队列的特点是:先进先出(FIFO)
BlockingQueue的方法
阻塞队列提供了四种处理方法:
| 方法\处理方式 |
抛出异常 |
返回特殊值 |
一直阻塞 |
超时退出 |
| 插入 |
add(e) |
offer(e) |
put(e) |
offer(e, time, unit) |
| 移除 |
remove() |
poll() |
take() |
poll(time, unit) |
| 检查 |
remove() |
peek() |
不可用 |
不可用 |
- 抛出异常:是指当阻塞队列满时候,再往队列里插入元素,会抛出IllegalStateException(“Queue full”)异常。当队列为空时,从队列里获取元素时会抛出NoSuchElementException异常 。
- 返回特殊值:插入方法会返回是否成功,成功则返回true。移除方法,则是从队列里拿出一个元素,如果没有则返回null
- 一直阻塞:当阻塞队列满时,如果生产者线程往队列里put元素,队列会一直阻塞生产者线程,直到拿到数据,或者响应中断退出。当队列空时,消费者线程试图从队列里take元素,队列也会阻塞消费者线程,直到队列可用。
- 超时退出:当阻塞队列满时,队列会阻塞生产者线程一段时间,如果超过一定的时间,生产者线程就会退出。
Java里的阻塞队列
- ArrayBlockingQueue :一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列,遵循FIFO原则。
- LinkedBlockingQueue :一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列,遵循FIFO原则,默认和最大长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE。
- PriorityBlockingQueue :一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
- DelayQueue:一个使用优先级队列实现的支持延时无界阻塞队列。
- SynchronousQueue:一个不存储元素的阻塞队列。
- LinkedTransferQueue:一个由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
- LinkedBlockingDeque:一个由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。
有界:有初始化最大长度,达到最大程度继续添加要莫阻塞,要莫抛出异常
无界:没有初始化最大长度,能够一直添加,不会阻塞或抛出异常,一直到OOM。
因为阻塞队列实现都差不多,我们就拿ArrayBlockingQueue来看下实现
ArrayBlockingQueue结构
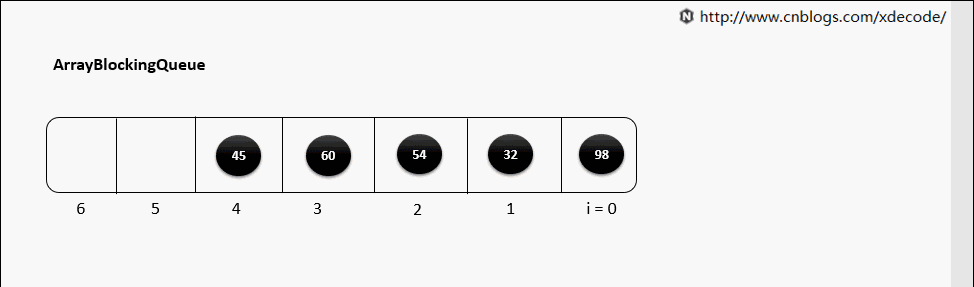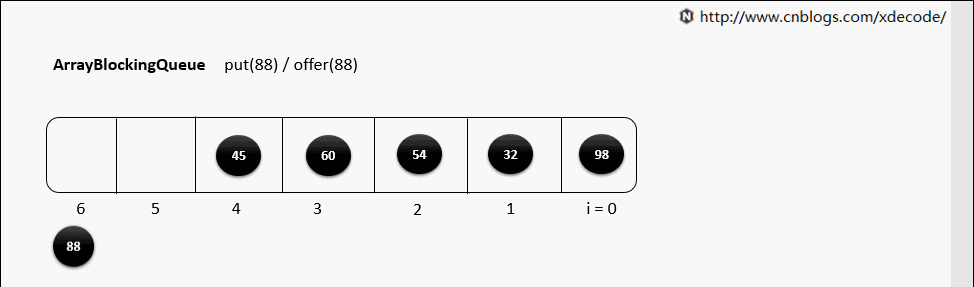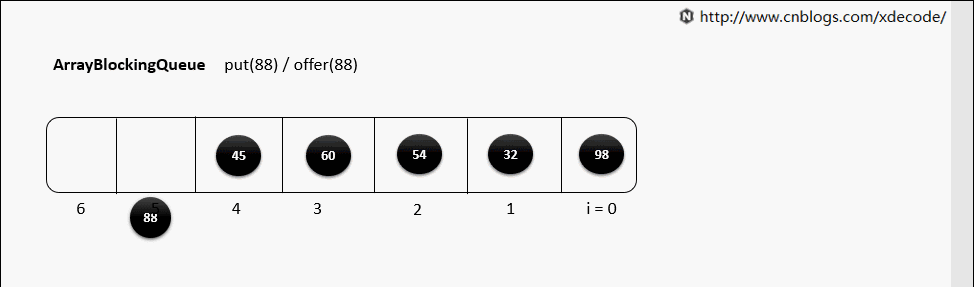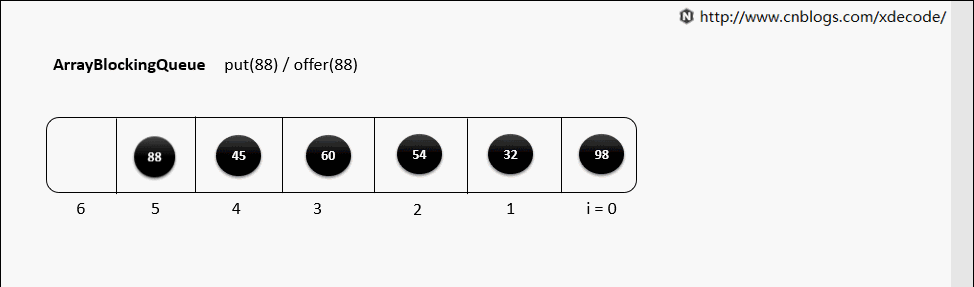
阻塞队列的实现都差不多,我们就拿ArrayBlockingQueue 来举例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private final E[] items;
private int takeIndex;
private int putIndex;
private int count;
final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Condition notEmpty;
private final Condition notFull;
|
构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
|
入队
offer不阻塞添加
在队尾插入一个元素, 如果队列没满,立即返回true; 如果队列满了,立即返回false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length) {
return false;
} else {
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
offer等待超时阻塞添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
enqueue(e);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
put阻塞添加
在队尾插入一个元素,如果队列满了,一直阻塞,直到数组不满了或者线程被中断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length) {
notFull.await();
}
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
这里使用的lock.lockInterruptibly() ,当前线程如果调用了Thread.interrupt()方法,那么lockInterruptible()判断的Thread.interrupted()聚会成立,就会抛出异常,其实就是线程中断,该方法就抛出异常。
enqueue入队操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private void enqueue(E x) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length) {
putIndex = 0;
}
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
}
|
队列没满items[putIndex] = data;达到数组长度重置putIndex,达到环形队列目的
出队
poll非阻塞出队
如果没有元素,直接返回null;如果有元素,将队头元素置null,但是要注意队头是随时变化的,并非一直是items[0]。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
poll 等待超时阻塞出队
从对头删除一个元素,如果数组不空,出队;如果数组已空且已经超时,返回null;如果数组已空且时间未超时,则进入等待,直到出现以下三种情况:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
take阻塞移除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
dequeue出队操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
private E dequeue() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length) {
takeIndex = 0;
}
count--;
if (itrs != null) {
itrs.elementDequeued();
}
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
|
使用场景
延时队列 DelayQueue
在我们的业务中通常会有一些需求是这样的
- 淘宝订单业务:下单之后如果三十分钟之内没有付款就自动取消订单。
- 饿了吗订餐通知:下单成功后60s之后给用户发送短信通知。
- 缓存系统,如果key到期了取出来删除
那么这类业务我们可以总结出一个特点:需要延迟工作。
由此的情况,就是我们的DelayQueue应用需求的产生。
看一个简单的例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| public class DelayedTask implements Delayed {
public DelayedTask(int delayedTime, TimeUnit unit, String message) {
this.delayedTime = delayedTime;
this.expireTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + (delayedTime > 0 ? unit.toMillis(delayedTime) : 0);
this.message = message;
}
private int delayedTime;
private long expireTime;
private String message;
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return expireTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
long d = (getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS));
return (d == 0) ? 0 : ((d < 0) ? -1 : 1);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "出队,延时:"+delayedTime+",消息:"+message;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Random random = new Random();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
DelayQueue<DelayedTask> delayedTasks = new DelayQueue<DelayedTask>();
executorService.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
String randomStr = RandomStringUtils.randomNumeric(10);
int randomTime = random.nextInt(10);
DelayedTask task = new DelayedTask(randomTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS, randomStr);
delayedTasks.add(task);
System.out.println("入队,消息:" + randomStr + "延时:" + randomTime + "秒");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
DelayedTask task = delayedTasks.take();
System.out.println(task);
}
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
float time = 0F;
while (true) {
System.out.println(time+"秒");
Thread.sleep(500);
time += 0.5;
}
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| 0.0秒
入队,消息:8675326967延时:5秒
0.5秒
入队,消息:8861554454延时:0秒
出队,延时:0,消息:8861554454
1.0秒
1.5秒
入队,消息:9123579697延时:1秒
2.0秒
2.5秒
出队,延时:1,消息:9123579697
入队,消息:5909478713延时:6秒
3.0秒
3.5秒
入队,消息:6287328130延时:0秒
出队,延时:0,消息:6287328130
4.0秒
4.5秒
出队,延时:5,消息:8675326967
入队,消息:4056656965延时:7秒
5.0秒
5.5秒
入队,消息:8250385270延时:9秒
6.0秒
6.5秒
入队,消息:1949026689延时:1秒
7.0秒
7.5秒
出队,延时:1,消息:1949026689
入队,消息:2952840210延时:9秒
8.0秒
8.5秒
|
总结
- ArrayBlockingQueue是有界的阻塞队列,不接受null
- 底层数据接口是数组,下标putIndex/takeIndex,构成一个环形FIFO队列
- 所有的增删改查数组公用了一把锁ReentrantLock,入队和出队数组下标和count变更都是靠这把锁来维护安全的。
- 阻塞的场景:1获取lock锁,2进入和取出还要满足condition 满了或者空了都等待出队和加入唤醒,ArrayBlockingQueue我们主要是put和take真正用到的阻塞方法(条件不满足)。
- 成员cout /putIndex、takeIndex是共享的,所以一些查询方法size、peek、toString、方法也是加上锁保证线程安全,但没有了并发损失了性能。
- remove(Object obj) 返回了第一个equals的Object
三种入队对比
- offer(E e):如果队列没满,立即返回true; 如果队列满了,立即返回false–>不阻塞
- put(E e):如果队列满了,一直阻塞,直到数组不满了或者线程被中断–>阻塞
- offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):在队尾插入一个元素,,如果数组已满,则进入等待,直到出现以下三种情况:–>阻塞
三种出对对比
- poll():如果没有元素,直接返回null;如果有元素,出队
- take():如果队列空了,一直阻塞,直到数组不为空或者线程被中断–>阻塞
- poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):如果数组不空,出队;如果数组已空且已经超时,返回null;如果数组已空且时间未超时,则进入等待,直到出现以下三种情况:
等待通知模式
这里面要理解等待/通知模式
阻塞队列使用了等待/通知的设计模式
标准范式
等待方
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public void wait() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (条件) {
condition.await();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
通知方
1
2
3
4
| public void notify() {
condition.signal();
}
|
等待超时模式
标准范式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public Integer wait(long time, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
long duration = timeUnit.toMillis(time);
lock.lock();
try {
while (duration > 0) {
duration += System.currentTimeMillis();
condition.await(time, timeUnit);
duration -= System.currentTimeMillis();
}
return null;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|


